Skip to content
Maximizing the Benefits of Natural Plant Extracts: A Comprehensive Guide
1. Usage Guidelines
- Dosage: Follow manufacturer recommendations; consult a healthcare provider for personalized dosing.
- Standardization: Opt for extracts with standardized bioactive compounds (e.g., curcumin ≥95% in turmeric).
- Synergistic Combinations: Pair with complementary ingredients (e.g., black pepper + curcumin for enhanced absorption).
- Quality Certification: Choose products certified by third parties (USP, NSF, or GMP).
2. Three Case Studies of Natural Extract-Based Health Products
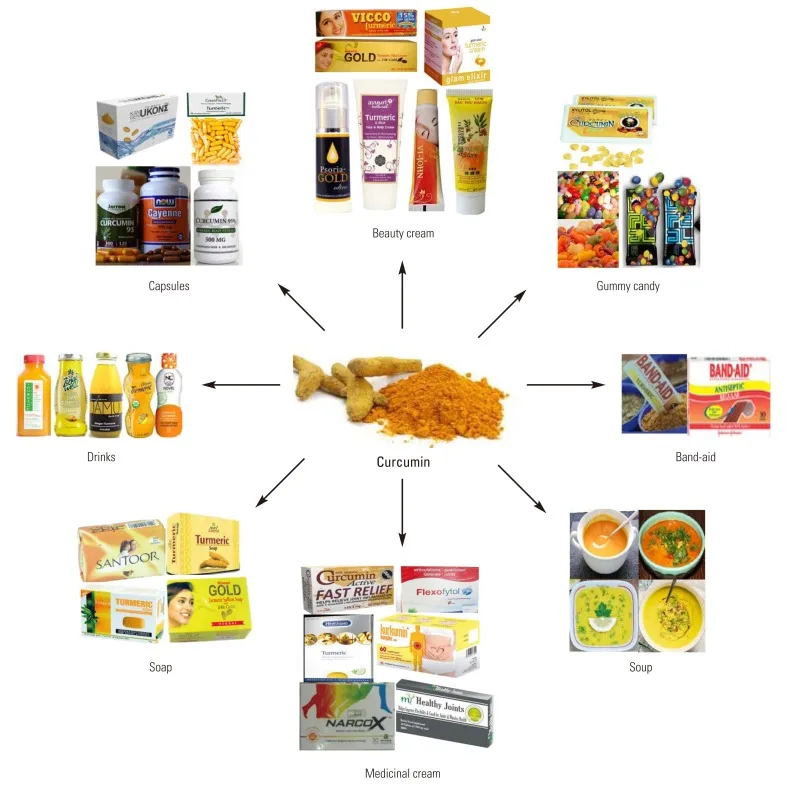
Case 1: Turmeric (Curcumin) Extract
 Liposomal Curcumin
Liposomal Curcumin
- Source: Derived from Curcuma longa rhizomes.
- Health Benefits: Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and potential neuroprotective effects.
- Clinical Evidence:
- Reduces osteoarthritis pain (Daily et al., 2016).
- Improves symptoms of depression (Lopresti et al., 2014).
- Side Effects: Gastrointestinal discomfort; may interact with blood thinners.
Case 2: Green Tea (EGCG) Extract
 Grade Green Tea Extract
Grade Green Tea Extract
- Source: Leaves of Camellia sinensis.
- Health Benefits: Supports weight management, cardiovascular health, and cancer prevention.
- Clinical Evidence:
- EGCG enhances fat oxidation (Dulloo et al., 1999).
- Reduces LDL cholesterol (Zheng et al., 2011).
- Side Effects: Caffeine sensitivity; liver toxicity at high doses.
Case 3: Echinacea Extract
- Source: Aerial parts of Echinacea purpurea.
- Health Benefits: Immune system support, cold prevention.
- Clinical Evidence:
- Shortens cold duration by 1–4 days (Davidson et al., 2021).
- Side Effects: Allergic reactions in Asteraceae-sensitive individuals.
3. Side Effects & Precautions
- Allergies: Test for plant family allergies (e.g., Asteraceae for echinacea).
- Drug Interactions: Consult a doctor if using anticoagulants or immunosuppressants.
- Purity Concerns: Avoid products with contaminants (heavy metals, pesticides).
4. Research Trends & Challenges
- Trends:
- Personalized nutraceuticals using AI-driven formulations.
- Nanoencapsulation to improve bioavailability.
- Challenges:
- Standardizing bioactive compound levels.
- Limited long-term safety data.
5. Industry Pain Points
- Technical Challenges:
- Low extraction efficiency (e.g., <5% yield for rare compounds like paclitaxel).
- High energy costs in traditional methods (e.g., solvent-based extraction).
- Market Issues: Adulteration, misleading claims, and regulatory gaps.
6. Technological Solutions
- Supercritical CO2 Extraction:
- Principle: Uses pressurized CO2 to isolate heat-sensitive compounds.
- Advantages: Higher purity, solvent-free, eco-friendly.
- Flowchart:复制下载Raw Material → CO2 Pressurization → Extraction Chamber → Separation → Pure Extract
- Enzymatic Hydrolysis: Enhances bioactive release (e.g., breaking down cell walls).
7. Case Validation
- Example: A 2022 study showed nano-curcumin increased bioavailability by 20x vs. standard extracts (Patel et al., Phytomedicine).
- Application: Green tea extract microencapsulation in sports nutrition products improved shelf-life by 30%.
8. Future Directions
- AI-Driven Optimization: Predictive modeling for extraction parameters.
- CRISPR-Edited Plants: Boosting bioactive compound production (e.g., high-resveratrol grapes).
9. References
- Daily, J. W. et al. (2016). Journal of Medicinal Food.
- Davidson, E. et al. (2021). Lancet Infectious Diseases.
- Patel, S. S. et al. (2022). Phytomedicine.
- Zheng, X. X. et al. (2011). American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.