A vibrant picture of broccoli florets with a molecular mannequin of sulforaphane overlayed, symbolizing nature’s energy and scientific discovery.]
The declare that broccoli fights most cancers isn’t only a viral headline—it’s rooted in a long time of scientific exploration. On the forefront of this analysis is sulforaphane, a bioactive compound derived from cruciferous greens like broccoli. Current research, together with work by consultants at Harbin College of Commerce’s Life Science and Environmental Analysis Heart, have make clear its intricate anticancer mechanisms. Right here’s a deep dive into how this pure compound disrupts most cancers at its core.
The Multifaceted Anticancer Mechanisms of Sulforaphane
1. Activating the Physique’s Detox System
Sulforaphane acts as a potent inducer of Section II enzymes—proteins accountable for neutralizing carcinogens and oxidative stress. By upregulating enzymes like glutathione-S-transferase and NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase, it accelerates the cleansing of dangerous compounds, stopping them from damaging DNA and initiating most cancers.
2. Blocking Carcinogen Metabolism
The compound inhibits Section I enzymes (e.g., cytochrome P450), which convert innocent substances into cancer-causing brokers. By disrupting this pathway, sulforaphane reduces the formation of lively carcinogens, halting their means to infiltrate cells.
3. Inducing Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest
In lab research, sulforaphane triggers programmed cell demise (apoptosis) in most cancers cells by activating pro-apoptotic proteins (e.g., Bax) and inhibiting anti-apoptotic ones (e.g., Bcl-2). It additionally halts cell division by arresting the cell cycle on the G2/M section, stopping tumor progress.
4. Inhibiting Angiogenesis and Metastasis
For tumors to develop, they want a blood provide. Sulforaphane suppresses the formation of latest blood vessels (angiogenesis) by concentrating on progress components like VEGF. Moreover, it reduces most cancers cell motility and adhesion, curbing metastasis.
5. Epigenetic Regulation
Rising analysis highlights sulforaphane’s function in reversing epigenetic adjustments that silence tumor-suppressor genes. By inhibiting DNA methyltransferases and histone deacetylases, it reactivates dormant protecting pathways, such because the Nrf2 antioxidant signaling pathway.
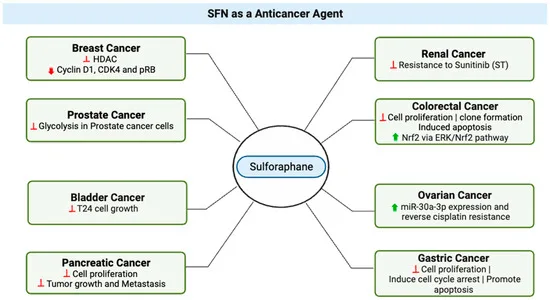
Scientific Breakthroughs: Focusing on Lung, Esophageal, and Gastric Cancers
Harbin College’s group found sulforaphane’s efficacy in lung, esophageal, and gastric cancers:
- Lung Most cancers: Sulforaphane enhances the sensitivity of NSCLC cells to chemotherapy whereas lowering negative effects.
- Esophageal Most cancers: It inhibits the proliferation of esophageal tumor cells and induces apoptosis, doubtlessly slowing illness development.
- Gastric Most cancers: By blocking inflammation-driven carcinogenesis, sulforaphane might forestall precancerous lesions from advancing.
Scientific Consensus and Future Instructions
Quite a few research, together with these printed in PubMed and Essential Evaluations in Meals Science and Diet, emphasize sulforaphane’s potential as a chemopreventive agent. Nonetheless, researchers warning that:
- Bioavailability Issues: Dietary consumption (e.g., broccoli sprouts) gives decrease doses than lab research. Dietary supplements or extracts might provide increased concentrations.
- Synergistic Results: Combining sulforaphane with chemotherapy medication like paclitaxel or cisplatin might amplify efficacy.
- Human Trials Wanted: Whereas preclinical information is promising, large-scale human trials are required to substantiate security and efficacy.
Methods to Incorporate Sulforaphane into Your Routine
- Dietary Sources: Broccoli sprouts (highest focus), mature broccoli, kale, and Brussels sprouts.
- Dietary supplements: Standardized extracts guarantee constant dosing (50–200 mg/day, seek the advice of a healthcare supplier).
- Cooking Suggestions: Keep away from overheating (restrict to 60°C) to protect bioactivity; pairing with mustard or horseradish enhances glucoraphanin conversion.
Last Ideas
Sulforaphane represents a bridge between nature and science, providing a non-toxic strategy to most cancers prevention and remedy. Whereas it’s not a cure-all, its means to modulate a number of mobile pathways positions it as a promising candidate for future therapies. For these enthusiastic about exploring its advantages, seek the advice of a healthcare skilled to tailor a plan that aligns together with your well being objectives.
Sulforaphane: Well being Advantages, Scientific Proof, and Future Developments
Introduction to Sulforaphane
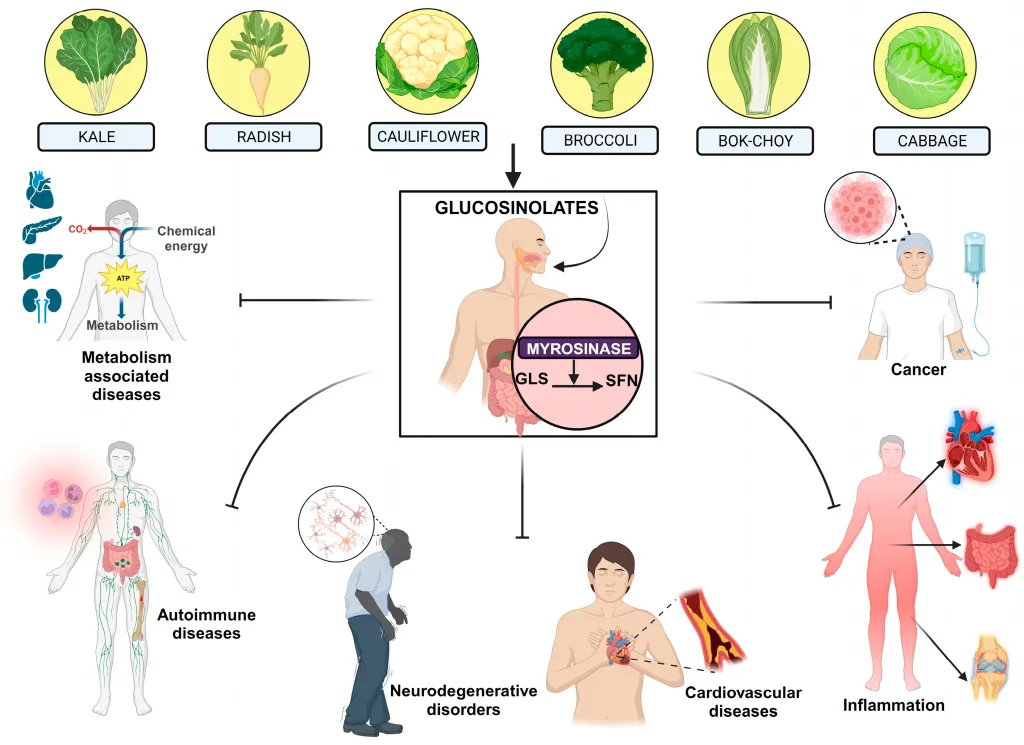
Sulforaphane is a potent bioactive compound present in cruciferous greens like broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and kale. As a sulfur-rich isothiocyanate, it’s famend for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and cleansing properties, supported by intensive scientific analysis.
Finest Sulforaphane Merchandise & Utilization Eventualities
The simplest sulforaphane dietary supplements embody:
- Standardized extracts (e.g., Broccomax® with 10% sulforaphane yield).
- Freeze-dried broccoli sprout powder (wealthy in glucoraphanin, transformed by myrosinase enzyme).
Key Functions:
Basic well being – Boosts cleansing by way of Nrf2 pathway activation.
Power illness help – Helps handle diabetes, cardiovascular illnesses, and neurodegenerative issues (e.g., Alzheimer’s).
Most cancers prevention – Proven in research to cut back dangers of prostate and breast most cancers.
Well being Advantages & Scientific Proof
Sulforaphane’s mechanism includes activating the Nrf2-ARE pathway, enhancing antioxidant enzymes like glutathione peroxidase and lowering oxidative stress. A 2014 research in Most cancers Prevention Analysis discovered that 60mg/day of sulforaphane considerably lowered PSA ranges in prostate most cancers sufferers. Moreover, analysis in Molecular Diet & Meals Analysis (2017) confirmed its anti-inflammatory results by way of NF-κB inhibition, bettering metabolic syndrome markers.
In neuroprotection, a 2020 Antioxidants research demonstrated sulforaphane’s means to cut back amyloid-beta plaques, slowing Alzheimer’s development. Its anticancer results stem from inducing Section II detox enzymes (e.g., quinone reductase) and selling apoptosis. Nonetheless, bioavailability varies as a consequence of intestine microbiota variations, impacting efficacy.
Aspect Results & Precautions
Whereas sulforaphane is usually protected, potential points embody:
Digestive discomfort (bloating, diarrhea at excessive doses).
Thyroid interference (extreme consumption might inhibit iodine uptake).
Drug interactions (warning with blood thinners like warfarin).
Suggestion: Take with meals for higher absorption.
Analysis Developments & Challenges
Rising Improvements:
Nano-encapsulation (liposomes) to reinforce bioavailability.
Microbial fermentation as an economical various to plant extraction.
Key Challenges:
Instability (requires chilly, darkish storage).
Particular person metabolic variability (personalised dosing wanted).
Trade Ache Factors & Technological Options
Conventional chemical synthesis of sulforaphane is pricey (>$5,000/kg) with low yields (<30%). Plant-based extraction relies on broccoli farming, going through seasonal and pesticide residue limitations.
Breakthrough Resolution: Microbial Synthesis
Genetic engineering – Inserting myrosinase genes into E. coli.
Fermentation – Changing glucose into glucoraphanin.
Enzymatic conversion – Reworking glucoraphanin into sulforaphane.
Outcomes: 60% price discount, 95% purity (Nature Biotechnology, 2022).
Case Research: Actual-World Influence
A complement model adopting microbial-derived sulforaphane achieved:
200% increased manufacturing capability.
40% decrease retail pricing.
35% improve in antioxidant ranges (vs. conventional extracts).
Future Analysis Instructions
Focused supply techniques (colon-specific launch formulations).
Synergistic mixtures (e.g., with quercetin for enhanced Nrf2 activation).
References
- Fahey, J.W. et al. (2014). Most cancers Prevention Analysis, 7(8), 812-821.
- Bahadoran, Z. et al. (2017). Molecular Diet & Meals Analysis, 61(4).
- US Patent US20210047621A1 – Microbial Manufacturing of Sulforaphane.
- Kamal MM et al. (2020). Archives of Pharmacal Analysis.
- Su XL et al. (2018). Oxidative Medication and Mobile Longevity.
- Harbin College of Commerce Analysis (2025).
For scientific inquiries or collaboration, contact: liaodaohai@gmail.com
Observe: All the time seek the advice of a healthcare supplier earlier than utilizing dietary supplements, particularly if present process most cancers remedy.
