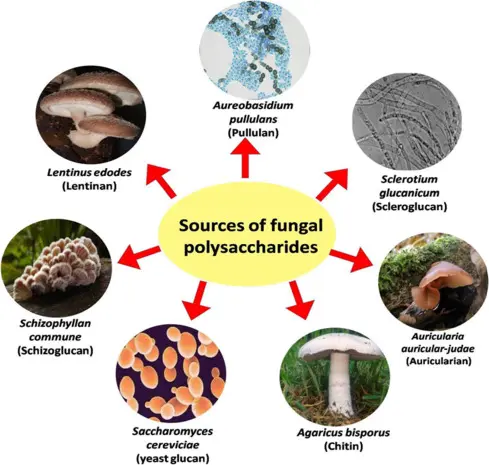
1. What are fungal polysaccharides?
Reply: Fungal polysaccharides are substances extensively present in fungal vegetation. They’re macromolecular compounds shaped by connecting a number of monosaccharide molecules and have a variety of pharmacological actions. They’re biologically prevalent substances with very important results.
2. Why do fungal polysaccharides have organic exercise?
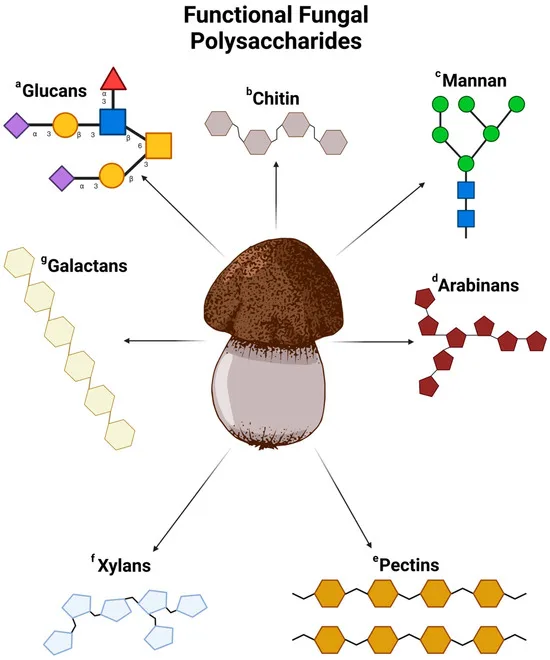
There are lots of sorts of polysaccharides. Polysaccharide molecules usually include many several types of monosaccharides. The association of monosaccharides may be very various. As a result of completely different preparations, the pharmacological actions of several types of polysaccharides are completely different.
There are 1:3 and 1:6 connection modes between monosaccharides in fungal polysaccharides. They’ve a spiral three-dimensional construction. Their configuration is much like DNA. They’re a β-type polysaccharide. Since there isn’t a β-type amylase within the physique, fungal polysaccharides is not going to be digested and decomposed after coming into the human physique. By way of absorption, fungal polysaccharides immediately bind to receptors on the cell membrane, thereby producing a variety of pharmacological actions.
3. Fungal polysaccharides have 18 pharmacological actions
1. Enhance the physique‘s immune operate;
2. Enhance the flexibility of bone marrow, spleen, and blood cells to synthesize DNA, RNA, protein, and different biologically energetic substances;
3. Enhance the oxygen carrying and nutrient provide of hemoglobin;
4. Enhance the liver’s detoxing capacity;
5. Anti-radiation and anti-chemical drug harm;
6. Enhance the physique‘s capacity to scavenge free radicals, speed up blood circulation, enhance the exercise of intracellular enzymes, and resist fatigue;
7. Enhance the phagocytic index of phagocytes by 30% to 40%, and enhance the phagocytic proportion by 30% to 60%;
8. Enhance NK cell exercise by 27% to 45%;
9. Enhance the ratio of T cells to B cells;
10. Bidirectionally regulate the humoral immunity stage of immunoglobulins (i.e., alter these which are too excessive or too low to regular);
11 , enhance the omnipotence of DNA, RNA and protein within the liver, spleen, bone marrow and blood by 30% to 60%;
12. Enhance the exercise of alcohol dehydrogenase and lactate dehydrogenase by 15% to 45%;
13. Enhance the oxygen carrying capability of blood by 20% to 40%;
14. Enhance superoxide dismutase by 17% to 35%, so it might considerably enhance the physique‘s illness resistance and vitality;
15. It could considerably enhance the flexibility to restore broken cells and tissues and liver detoxing for tumors, frequent colds, bronchial asthma, immune allergy symptoms, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, congestion, diabetes, neurasthenia, meals poisoning, environmental air pollution poisoning, broken cells and tissues, and liver detoxing;
16. With using antibiotics, it might remove the uncomfortable side effects of antibiotics, enhance the efficacy, and has a variety of drug enhancement results;
17. With radiotherapy and chemotherapy, it might enormously cut back uncomfortable side effects and considerably enhance the efficacy of radiotherapy and chemotherapy.
18. It could regulate quite a lot of cultural ailments associated to trendy social residing habits and environmental air pollution.
4. Why are medicinal edible fungi probably the most preferrred well being meals within the twenty first century?
As a result of each medicinal and edible fungi include wealthy practical elements – polysaccharides. They’ve the capabilities of adjusting the physiological capabilities of the physique, decreasing blood stress, decreasing blood viscosity, decreasing ldl cholesterol, decreasing blood lipids, enhancing myocardial contractility, bettering blood oxygen provide capability, accelerating blood microcirculation, bettering enzyme exercise, calming and tranquilizing the thoughts, bettering liver physiological capabilities and detoxing capacity, bettering the flexibility of the liver, bone marrow, and blood to synthesize DNA, RNA, and protein, activating cells to revive the capabilities of varied organs and tissues, restoring the steadiness of the physique, bettering the vitality of the physique, and successfully bettering illness resistance. On the identical time, it is a perfect therapeutic product with none poisonous uncomfortable side effects. It’s “secure, non-toxic, and efficient“. It’s a clever selection to decide on fungal plant meals and keep your individual well being.
5. The distinction between fungal polysaccharide meals and medication:
Drugs: single prescription, chemical composition, therapy, quick efficacy, robust concentrating on, symptomatic therapy, poisonous uncomfortable side effects,.
Fungal polysaccharides: meals compound, compatibility mixture, dietary complement, regulating the yin and yang steadiness of human organs, no poisonous uncomfortable side effects. The impact is comparatively sluggish, treating each the signs and the foundation trigger.
Medicine: One is therapy, which is to deal with the signs.
Meals: One is conditioning, which is to deal with the foundation trigger, and meals remedy is best than drug remedy.
6. Is the twenty first century the period of fungal polysaccharides?
Consultants on the tutorial change assembly held by the Chinese language Society of Microbiology and the Chinese language Society of Bioengineering in October 1995 identified that fungal polysaccharides are the most effective well being merchandise within the twenty first century. The World Well being Group has positioned edible fungi as practical factor-type well being meals. International consultants say that the protein period within the twenty first century will inevitably give approach to the fungal polysaccharide period.
7. Fungi and fungal polysaccharides
When mentioning fungi, individuals naturally consider issues like mushrooms and Ganoderma lucidum. Fungi and fungal polysaccharides are certainly two completely different ideas. It takes a number of tons of fungi to extract a number of kilograms of polysaccharides, and its value is way increased than gold.
8. High quality of fungal polysaccharide meals

Fungal polysaccharide meals primarily include energetic polysaccharide elements that play an necessary function in regulating human immunity.
Core Capabilities

Customized Formulations: Tablets | Capsules | Gummies | Powder | Liquids